VideoLLaMB: Long-context Video Understanding with Recurrent Memory Bridges
ICCV · 2025 · arXiv: arxiv.org/abs/2409.01071
Abstract
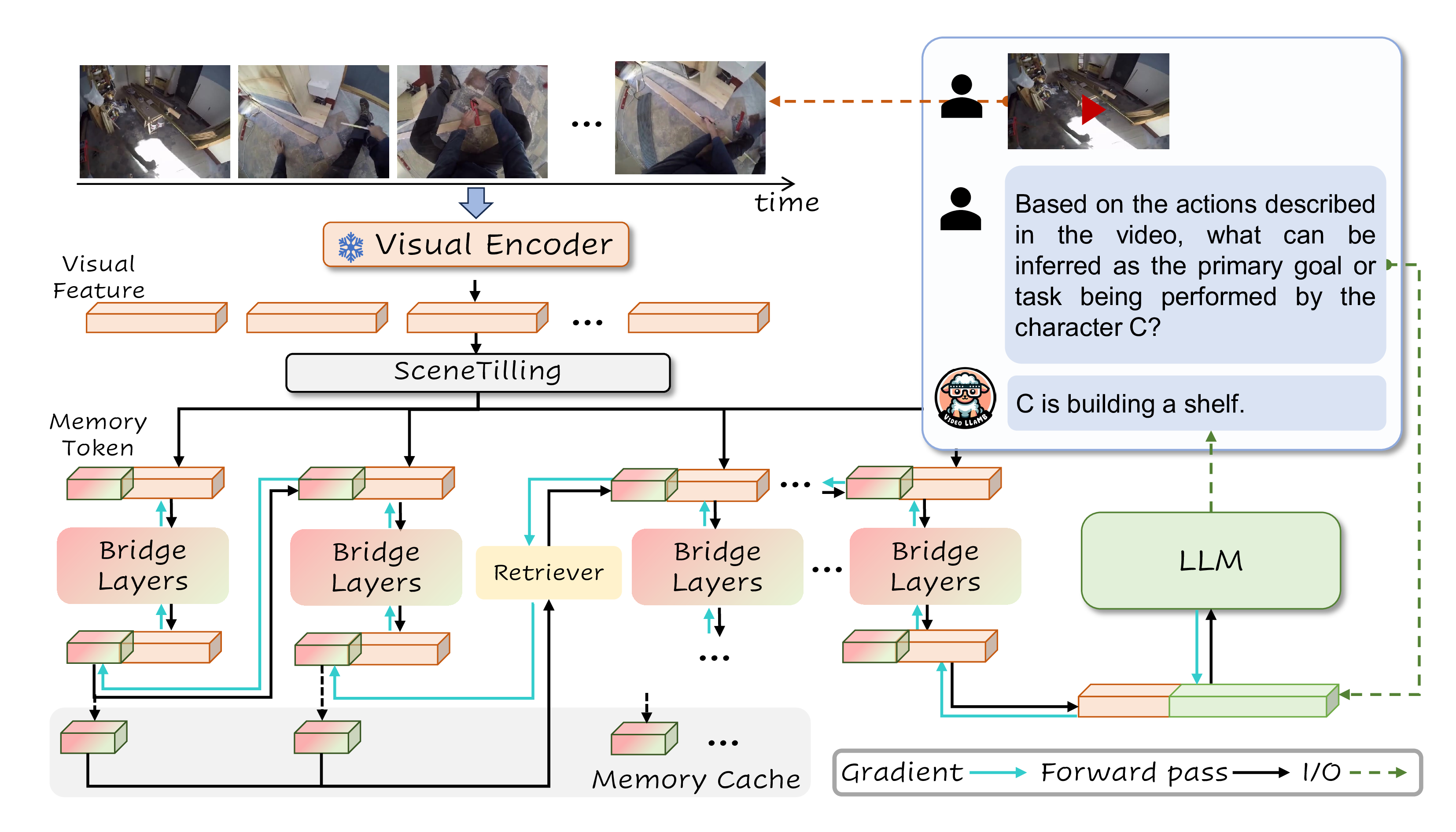
Recent advancements in large-scale video-language models have shown significant potential for real-time planning and detailed interactions. However, their high computational demands and the scarcity of annotated datasets limit their practicality for academic researchers. In this work, we introduce VideoLLaMB, a novel framework that utilizes temporal memory tokens within bridge layers to allow for the encoding of entire video sequences alongside historical visual data, effectively preserving semantic continuity and enhancing model performance across various tasks. This approach includes recurrent memory tokens and a SceneTilling algorithm, which segments videos into independent semantic units to preserve semantic integrity. Empirically, VideoLLaMB significantly outstrips existing video-language models, demonstrating a 5.5 points improvement over its competitors across three VideoQA benchmarks, and 2.06 points on egocentric planning. Comprehensive results on the MVBench show that VideoLLaMB-7B achieves markedly better results than previous 7B models of same LLM. Remarkably, it maintains robust performance as PLLaVA even as video length increases up to 8 times. Besides, the frame retrieval results on our specialized Needle in a Video Haystack (NIAVH) benchmark, further validate VideoLLaMB’s prowess in accurately identifying specific frames within lengthy videos. Our SceneTilling algorithm also enables the generation of streaming video captions directly, without necessitating additional training. In terms of efficiency, VideoLLaMB, trained on 16 frames, supports up to 320 frames on a single Nvidia A100 GPU with linear GPU memory scaling, ensuring both high performance and cost-effectiveness, thereby setting a new foundation for long-form video-language models in both academic and practical applications.
Citation
@inproceedings{wang2025videollamb,
title={VideoLLaMB: Long-context Video Understanding with Recurrent Memory Bridges},
author={Yuxuan Wang and Cihang Xie and Yang Liu and Zilong Zheng},
year={2025},
booktitle={International Conference on Computer Vision},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.01071},
}